

Many couples willing to have their own child are still unable to become pregnant after the first line of therapy such as ovulation induction, intrauterine insemination, or reproductive surgery. For these couples, the next logical step is to explore the Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) like In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) popularly known as Test Tube Baby.
IVF is an Assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedure used to treat a range of fertility problems. In IVF Treatment , the process of fertilization occurs outside the female body. A woman’s eggs are surgically removed from her ovaries via egg collection procedure, and fertilized with sperm in laboratory. Once the egg is fertilized, the egg is implanted into the woman’s womb.
The reasons are compelling. With this approach we can transfer a single normal embryo and expect pregnancy rates that are better than most clinics with transfer of 2 or even 3 embryos. The miscarriage rate is marked lower, and the chances of a healthy full-term pregnancy are higher.
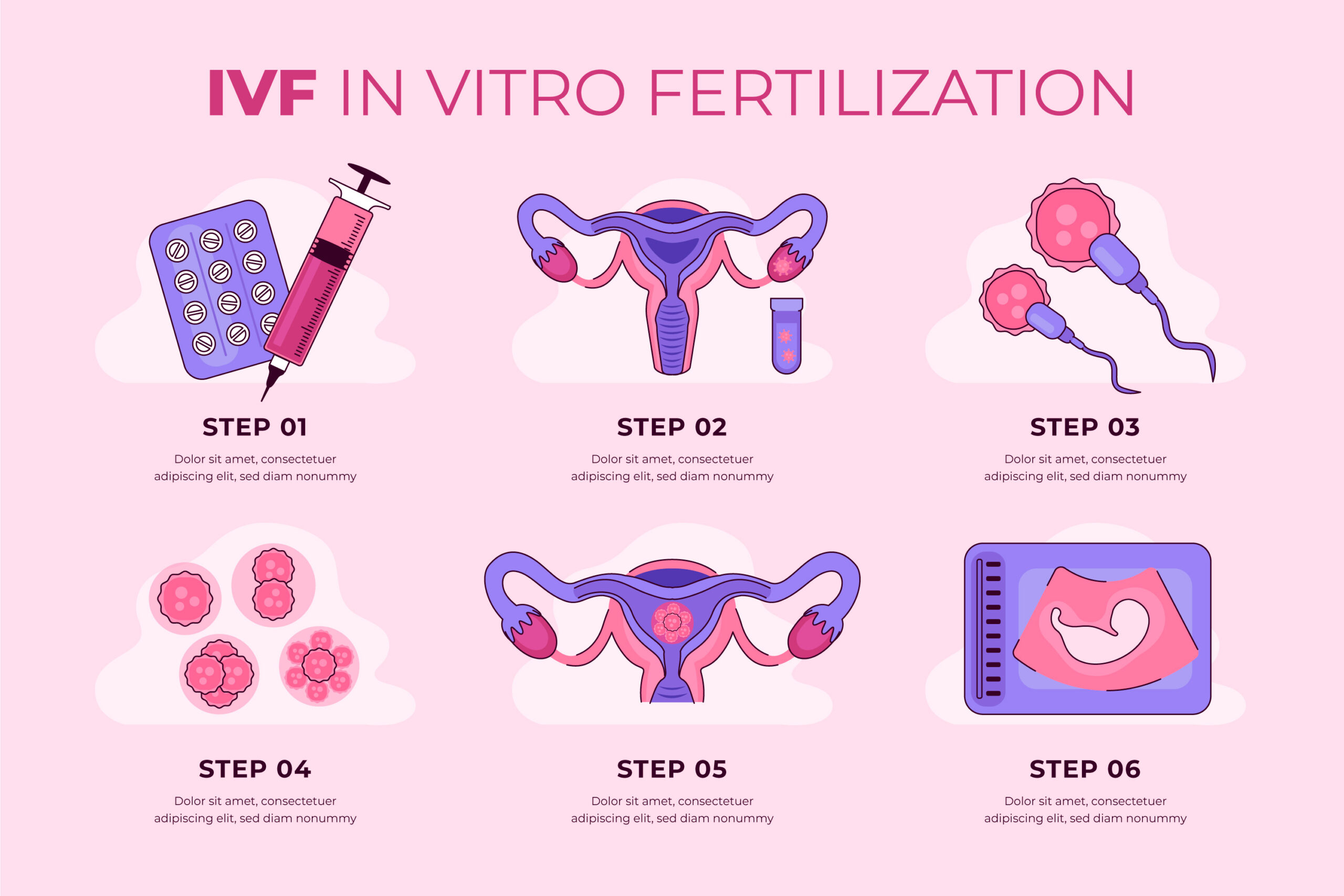
To achieve pregnancy as a result of IVF, several steps are necessary. Each one of them is described in detail to help you understand the treatment as it occurs.
The first stage of the process consists of suppressing ovarian function by administering an oral contraceptive and/ or a medication that inhabits pituitary gland function. This stage is not always required as you doctor determines if you need it or not. During the suppression phase , the levels of estrogen becomes very low, similar to menopause, which leads to some of the side effects, such as hot flashes.
Ovarian suppression is reached when the estradiol level is sufficiently low, as described in Stage 1. At this time, ovarian stimulation can begin in order to achieve an “artificial cycle”. Your ovaries usually produce and release a single egg per cycle. Although this is sufficient for natural conception, conception with IVF usually requires more. This is achieved by ovarian hyperstimulation. These medications stimulate the development of several ovarian follicles resulting in the retrieval of more eggs.
When follicles are large enough and when hormonal levels are adequate, it is time to trigger the ovaries to prepare the eggs for maturation and ovulation. The trigger is done by injecting hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, a pregnancy hormone similar to LH) or a recombinant hormone.
Eggs are retrieved transvaginally under ultrasound guidance. Having located the mature follicles, the physician will insert a needle, attached to the probe, into each follicle and aspirate the fluid from each of them. You are given a local anesthetic and a sedative through an i.v. (intravenous) infusion. If you are interested, you may watch the procedure on the ultrasound monitor. The embryologist analyzes the contents of every follicle under the microscope. Once the procedure is completed, you are told how many eggs were retrieved. On that same day, these eggs will be combined with the sperm, In Vitro, should fertilize and then form the embryo.
Embryo transfer entails placing one or more embryos (usually one) inside the patient’s uterine cavity usually on cycle day 5. It requires a full bladder for better visualization with the abdominal ultrasound probe.
Here at PARIVAAR IVF CENTRE, we are quick to adopt cutting edge ideas and approaches when it is clear it is better. In freeze-all protocols all suitable embryos obtained from a “fresh” IVF cycle are frozen on either day 5 or 6 with no embryos being transferred that cycle. The transfer will then be planned for a later date in a separate FET cycle.
Preservation of sperm and embryos has its own significance in IVF. In some situations semen freezing becomes absolute necessity. e.g. male partner is not available at the time of Ovum Pick up or female partner is coming from out of country, in those males where sperm count is very low or males having ejaculatory dysfunction or those undergoing chemotherapy in near future etc. in such cases their semen can be effectively frozen and used for IVF.
During IVF, excess eggs are obtained as a result of patient’s response to the stimulation protocol. This may result in getting more than 3 embryos. As, it is not advisable to transfer more embryos, which may result in multiple pregnancies, it becomes necessary to cryopreserve these excess embryos. In case if patient doesn’t become pregnant in fresh cycle, she can take her frozen embryos in subsequent cycle.